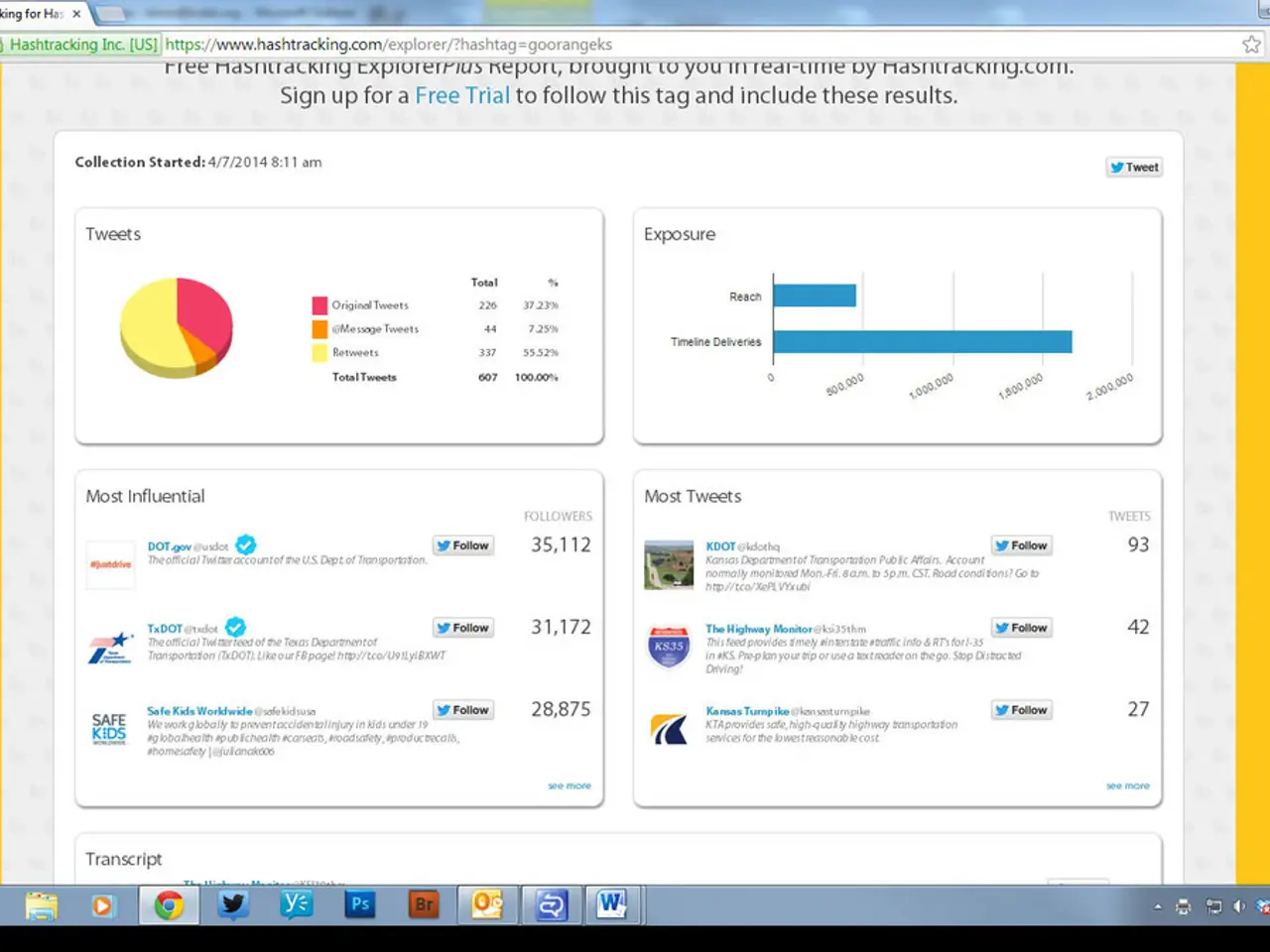
Topic Discussion: Use of Keywords in Content Creation
The C programming language is renowned for its efficiency and versatility, thanks in part to its set of reserved words known as keywords. These keywords, predefined and serving specific purposes, are integral to writing C programs. Here's a comprehensive list of keywords in C and their descriptions:
| Keyword | Description | |-----------------|----------------------------------------------| | **auto** | Automatically allocated memory | | **break** | Terminates a loop or switch statement | | **case** | Part of a switch statement | | **char** | Defines a character type | | **const** | Declares a constant variable | | **continue** | Skips to the next iteration of a loop | | **default** | Specifies a default case in a switch statement| | **do** | Part of a do-while loop | | **double** | Defines a double precision floating point type| | **else** | Part of an if-else statement | | **enum** | Defines an enumeration | | **extern** | Declares external variables or functions | | **float** | Defines a floating point type | | **for** | Defines a for loop | | **goto** | Jumps to a label | | **if** | Part of an if-else statement | | **int** | Defines an integer type | | **long** | Defines a long integer type | | **register** | Requests the compiler to store a variable in a register| | **return** | Returns control to the calling function | | **short** | Defines a short integer type | | **signed** | Declares a signed integer type | | **sizeof** | Returns the size of a data type or variable | | **static** | Preserves variable value across function calls| | **struct** | Defines a structure (custom data type) | | **switch** | Implements a multi-way branch | | **typedef** | Defines a new data type name | | **union** | Declares a union (overlapping memory structure)| | **unsigned** | Declares an unsigned variable (no negative values)| | **void** | Specifies no return value for a function | | **volatile** | Tells the compiler not to optimize the variable| | **while** | Used to create a while loop |
These keywords cannot be used as identifiers for variables, functions, or other program elements.
- The float keyword specifies the datatype used to declare a decimal type variable with 7 decimal digits precision. - The continue keyword skips to the next iteration of the loop. - The break keyword is used to terminate the innermost loop. - The register keyword tells the compiler to store variables in the CPU register instead of memory, for faster access. - The goto keyword is used to transfer the control of the program to the given label, allowing a jump from anywhere to anywhere within a function. - The union keyword is used as a user-defined data type, where all data members declared under the union keyword share the same memory location. - The static keyword is used to create static variables, which are not limited by a scope and can be used throughout the program, and whose value is preserved even after its scope. - Most keywords are in lower case, while identifiers follow various naming conventions. - The default keyword is used to specify case that is executed when no case value is matched in a switch statement. - The switch keyword in C is used as an alternate to the if-else ladder statement. - Keywords contain only alphabetic characters, while identifiers are a mix of characters, digits, and underscores. - The char keyword in C is used to declare a character variable. - The struct keyword is used to declare a structure, which is a list of variables (of different data types) grouped together under one data type. - The return keyword returns a value to where the function was called. - The double keyword specifies the datatype used to declare a decimal type variable with 15 decimal digits precision. - The do keyword is used to declare a do-while loop, which executes once and then checks its condition to see if it should continue through the loop. - The case keyword allows us to execute different code for different possible values of a single variable in a switch statement. - The keywords in C programming language are predefined or reserved words that have special meanings to the compiler and cannot be used as identifiers in the program. - Keywords are the words that have predefined specific meanings, while identifiers are the placeholders of the data types. - The for keyword is used to declare a for-loop, which runs a certain number of times. - The const keyword defines a variable whose value cannot be changed. - The sizeof keyword gets the size of an expression (variables, arrays, pointers, etc.) in bytes. - The enum is a user-defined datatype that holds a list of user-defined integer constants. - The while keyword is used to declare a while loop that runs till the given condition is true. - The int keyword is used to give a variable an integer type, with a range of at least -32768 to +32767.
- The keyword specifies the data type used to declare a decimal type variable with 7 decimal digits precision.
- The keyword skips to the next iteration of the loop, without executing the remaining statements within the current loop iteration.